Introduction
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) is an analytic technique for elemental analysis and trace metals in a sample. The principle of AAS is that atoms or ions absorb light of a particular wavelength. Every element uniquely absorbs the wavelength, and measuring absorbance measurement helps determine the concentration of elements in the sample according to standards.
Scope
AAS (Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy) has many applications and has emerged as one of the popular methods for trace metals analysis. It has also become an essential method for quantitive detection of elemental concentration. The other crucial techniques for evaluating the elemental composition at low sample volumes are Falme atomic absorption spectroscopy(FASS) and Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy(GFAAS).
Difference between AAS and GFAAS
| Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy | Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy |
| The sample should be in liquid form. | This technique requires smaller volumes of samples. |
| It has a lower sensitivity and is suitable for higher concentrations. | It has a higher sensitivity and is suitable for lower concentrations. |
| It assists manufacturers in routine analysis. | It is a time-consuming process but can detect trace metals. |
Test Procedure
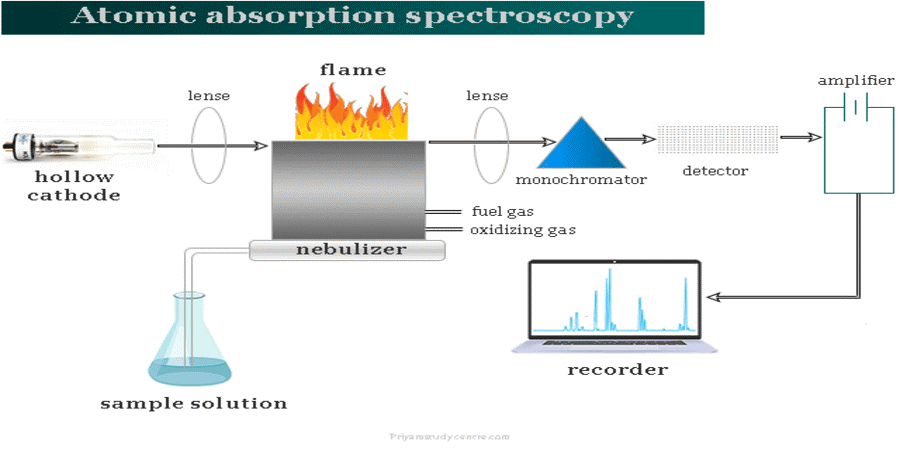
Expose the sample to a radiation source of defined wavelengths. If any absorption is done, the measurement of absorbance reveals that the intensity of light is reduced in some regions of the spectrum. The reduction in intensity allows elemental analysis of the sample. The characteristics of the element present in the sample are identified.
Later, the sample is subjected to different light sources, resulting in a dispersion of wavelengths. Thus, the quantitative detection of the sample’s elemental concentration is measured using the AAS detectors. Furthermore, an unknown sample can be evaluated quantitatively by comparing the obtained results with reference standards, facilitating flame atomization.
Sample Details
The ASS technique can be applied to both liquid and solid samples. The Liquid samples can be analyzed directly without any treatment. On the contrary, the solid samples are crushed and changed to a solution. Conversely, some of the solid samples can be analyzed directly according to the sample’s viscosity. In the case of FAAS analysis, the sample’s viscosity should be the same as that of water. Nebulizers are designed to attain the desired viscosity.
Result Analysis
AAS is an important analytical technique used in the detection of trace metals for quality control purposes in most industries. Its capacity for accurate elemental analysis undergirds regulatory compliance and safety at every level of product quality.
Applications of Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)
Here are applications of Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)
- Trace Metal Analysis: AAS can detect trace metals in every sample form, making it necessary for environmental monitoring, food safety, and clinical diagnostics.
- Quality Control in Manufacturing: Industries are allowed to use AAS for normal quality control operations, which ensures that the products comply with the regulations. The technology accurately quantifies elemental concentrations in raw materials and finished products.
- Environmental Testing: AAS can be used to test soil and water for potential heavy metal contamination. The analysis thus provides a basis for pollution control and environmental protection.
- Geochemical Analysis: AAS is a commonly applied tool in geological research to determine the mineral composition of samples and find resources.
- Food Industry: In food industries, AAS can determine metals that are harmful to health, such as those present in food (such as lead or mercury), helping to detect products with unhealthy levels of these substances to ensure consumer safety and meet regulatory requirements.
With AAS, industries improve analytical accuracy, product quality, and continued efficiency in health and safety requirements.
Conclusion
AAS is a vital tool in elemental analysis that ascertains the elemental composition in wide concentration ranges. It helps handle different samples and offers quality results. A boost in both manufacturers and industries improves quality control, regulatory compliance, and product development. Integrate AAS into your analytics to enhance precision and raise the bar higher in this industry.
FAQs
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) is an analytic technique for elemental analysis and trace metals in a sample.
It is based on the principle that atoms or ions absorb light of a particular wavelength.
AAS works by exposing a sample to a light source of defined wavelengths. The sample absorbs the light at characteristic wavelengths, and the drop in light intensity identifies and quantifies elements within it.
AAS presents an accurate and reliable elemental analysis. It is thus the basis for quality assurance to meet regulatory requirements and in product development. It assists in ensuring that high standards and consistency are maintained throughout the manufacturing process.
1. Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy 2. Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy
3 Easy Steps to Start Testing
Case Studies
In-depth examination of genuine material testing solutions
Dopant and ultra-low concentration elemental analysis using Scanning…
EELS analysis of gate and channel is performed on fin field-effect transistors (finFETs). Scanning transmission electron...
Read Case StudyAnalysis of degradation of PVC pipe using Fourier…
Introduction PVC is the polymer primarily used to make pipes for plumbing, drainage, and electrical conduits....
Read Case StudyNano-scale roughness measurement of Si-wafers by Atomic Force…
Nano-scale surface roughness is a critical parameter in fabricated thin-films that are used in optics, solar...
Read Case StudyTalk to Our Experts Today!
Submit your contact info and we’ll get back to you within 24 hours








