
Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS-MS) is a microanalytical technique that provides superior selectivity sensitivity and detail compared to GC with a single MS (GC-MS). It’s a sophisticated analytical technique that separates gas chromatography with detection using tandem mass spectrometry. It is one of the techniques that have widely been used to analyze complex mixtures, particularly in identifying and quantifying volatile and semivolatile organic compounds. This two-stage mass spectrometry approach offers improved selectivity and sensitivity for compound detection, even against a very complex sample matrix.
The field of GC-MS-MS (Gas Chromatography-mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry) is broad. It has many uses, including forensic research, food safety, pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, and clinical diagnostics. The technique is significant for detecting contaminants, drugs, pesticides, and pollutants at trace levels. This technique is also applied to complex biological samples’ blood and urine analysis.
Gas chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS-MS) is a configuration that uses a GC followed by two Mass Spectrometers with the same type of mass analyzer. The GC-MS-MS overcomes the limitations of GC with a single MS (GC-MS) and is used to analyze a variety of volatile organic species.
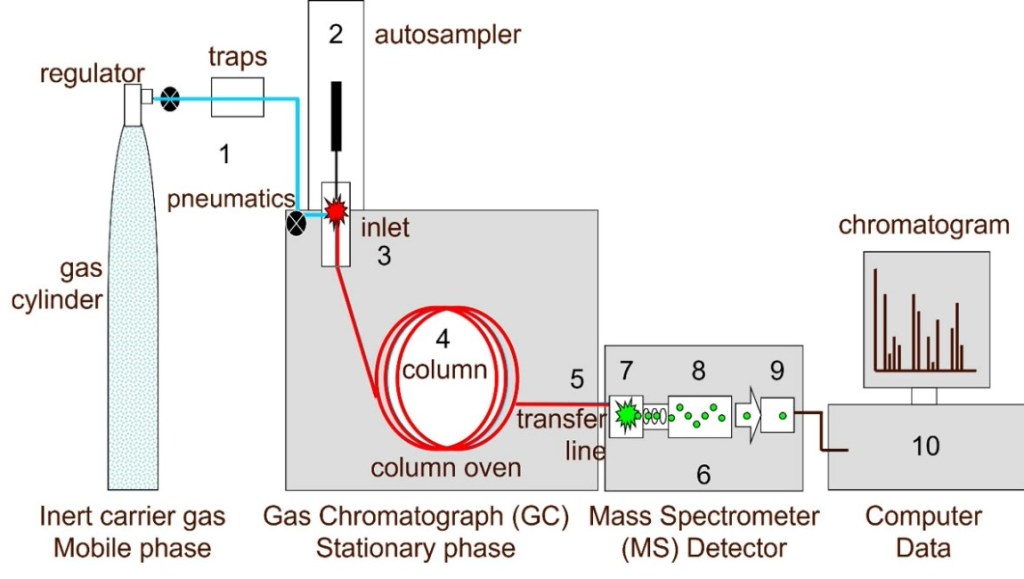
Gas Chromatography
Gas Chromatography utilizes the principle that intermolecular (physical adsorption) forces between molecules in a gas and a solid surface depend upon the molecular structure and the nature of the solid surface.
Mass Spectrometry
Mass Spectrometry works by ionizing chemical compounds to generate charged ions with a range of molecular masses. These ions are then separated based on their mass-to-charge (m/z) ratios and analyzed using spectrometry.
What is Tandem Mass Spectrometry?
In a Tandem MS system (MS-MS), the ions (termed precursor ions) that are separated in the first mass analyzer enter a collision cell for further fragmentation. Further, the collision cell is filled with a suitable inert gas, where an oscillatory field induces collisions between the precursor ions and inert gas molecules. This causes bond breakage in the precursor ions to form product ions. The product ions undergo further separation in the second mass analyzer, yielding more information and reducing interference and background noise.
| Particulars | Details |
| Size and Weight | Benchtop systems typically require a footprint of 1–2 square meters. |
| Power | Usually 120/240 V AC, 50/60 Hz |
| Temperature | Typically requires a stable temperature environment (20–25°C) and low humidity for optimal performance |
| Molecular ions | 1050 m/z |
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-mass spectrometry (GC-MS-MS) is a powerful analytical technique widely used for detecting and quantifying compounds in complex mixtures. In addition, it provides high sensitivity and specificity. Moreover, GC-MS-MS helps identify trace compounds with great precision.
| Advantages | Limitations | Applications |
| Extremely sensitive and accurate technique | GC-MS-MS allows the selection of specific analytes for individual fragmentation | Research and development Quality control Toxicology studies |
| GC-MS-MS allows selection of specific analytes for individual fragmentation | The high temperatures (300°C) used in the GC-MS injection port (and oven) can cause thermal degradation of injected molecules, affecting accuracy. | GC-MS-MS allows more complex mixtures to be analyzed more readily |
| GC-MS-MS allows more complex mixtures to be analysed more readily | GC-MS-MS is generally more suited for small to moderately sized molecules, and may not be suitable for larger biomolecules like proteins or large polymers. | Forensics Drug abuse prevention Odor analysis of foodstuffs |
GC-MS-MS is, thus, one of the most powerful analysis techniques; for this reason, it finds broad applications in research and industry. Still, GC-MS-MS has specific limitations, especially the necessity to operate with volatile samples and complicated instrumentation. In return, its advantages are sensitivity, specificity, and the possibility to analyze complex mixtures. Further, GC-MS-MS was an extremely new technology and thus had few applications to offer. Still, as technology continues to improve, its applications will expand more and more, being one of the most essential techniques in analytical chemistry.
It works by heating a liquid sample until it converts into a vapor that a gas like helium or hydrogen can carry. The gas (called a carrier gas or mobile phase) transports the sample through a long, thin glass or metal tube (column) that is coated with a chemical (stationary phase).
The selectivity and sensitivity of GC–MS/MS and HPLC–MS/MS are extremely high, and the structural information obtained from these techniques is extensive.
The sample will typically (although only sometimes) be in liquid form. Samples frequently extracted via SPE include biological samples such as urine, saliva, and plasma, environmental samples such as water, and food products such as beverages.
In-depth examination of genuine material testing solutions
EELS analysis of gate and channel is performed on fin field-effect transistors (finFETs). Scanning transmission electron...
Read Case StudyIntroduction PVC is the polymer primarily used to make pipes for plumbing, drainage, and electrical conduits....
Read Case StudyNano-scale surface roughness is a critical parameter in fabricated thin-films that are used in optics, solar...
Read Case StudySubmit your contact info and we’ll get back to you within 24 hours