ASTM G65 Introduction
ASTM G65 is a crucial standard in material science for understanding a material’s resistance to abrasion. It is a prominent test method for evaluating a material’s susceptibility to scratching and wear caused by abrasion with dry sand. The ASTM G65 dry sand/rubber wheel abrasion test employs a dry sand/rubber wheel apparatus to determine abrasion. Abrasive wear is a significant issue in many manufacturing, construction, and mining industries, as it can damage machinery or equipment, increase maintenance costs, and ultimately reduce production.
Scope of ASTM G65
ASTM G65 abrasion test centers around deciding the scratch opposition of metallic materials against a controlled grating power. This test is vital for materials in applications that experience continuous sliding contact with grating particles. For example,
- ASTM G65 test with stainless steel
- Development materials such as Building parts like lines, cladding, and latches,
- Car parts include Motor parts, pinion wheels, and valve train parts.
- Aviation parts, such as landing and parts, are presented in rigid natural circumstances.
The ASTM G65 test evaluates a material’s protection from scratching under controlled conditions, helping to choose reasonable materials for different applications and anticipate their wear execution.
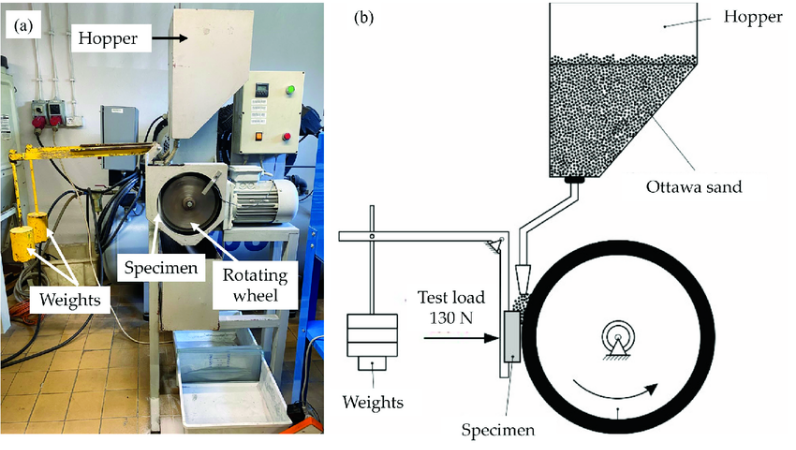
ASTM G65 Test Procedure
The ASTM G65 test methodology includes a dedicated apparatus with a rotating drum and a component for holding the test sample. The critical stages are below.
- Test Planning: Researchers prepare a flat, representative sample of the evaluated material according to standard specifications. This process may involve cleaning the sample and achieving a specific surface finish.
- Rough Determination: Researchers use a standardized grade of dry silica sand with a controlled particle size distribution as the abrasive material.
- Test Arrangement: The test sample is mounted safely on a holder in the machine. A pre-stacked elastic wheel lies against the surface of the sample.
- Scraped spot Cycle: Researchers then turn the elastic wheel into a revolution, creating controlled grating contact between sand particles and the sample’s surface. During this test, they can adjust the duration and number of cycles according to the desired degree of abrasion.
- Wear Assessment: After completing the scraped spot cycle, researchers check the sample for scratches and wear marks. They can also measure the depth and width of the scratches using profilometry techniques or specialized microscopy.
- Adhering strictly to the strategies illustrated in ASTM G65 guarantees the repeatability and precision of the experimental results.
ASTM G65 Data Analysis
The essential information acquired from the ASTM G65 test is subjective, given the presence and seriousness of scratches on the test sample. Nonetheless, quantitative estimations of scratch profundity and width can be utilized to make a wear profile. The following methods can decipher the outcomes.
Negligible or No Scratches: This material demonstrates phenomenal scratch resistance, suggesting it is appropriate for applications with high grating wear potential.
Shallow Scratches: It recommends moderate scratch resistance and is reasonable for applications with lower levels of rough wear.
Profound Scratches: Indicates poor scratch resistance, potentially requiring surface treatments or selecting a more wear-resistant material.
Finally, by analyzing the scratch samples and wear profiles, designers and material researchers can gain valuable insights into a material’s vulnerability to scratching and predict its performance in real-world applications.
ASTM G65 Test Specimens
| Sample details | The ASTM G65 test method can be applicable to a variety of materials, including metals, ceramics, plastics, and composites. |
| Sample size | Acceptable specimens are rectangular with a thickness of 3 to 25 mm and a surface area of 25 to 100 cm². |
| Sample preparation | Specimens shall be suitably prepared so they are flat or gently curved, free from surface defects, scratches, and other damage. |
The ASTM G65 standard indicates suggested aspects for the test sample. Utilizing a sample that is too small can prompt deluding results because of the expected non-delegate inspection of the material’s general scratch opposition. Moreover, the sample’s surface completion can impact the experimental outcomes. For example, a harsher surface completion could show a higher inclination for beginning scratching with a smoother surface.
Conclusion
Therefore, the ASTM G65 test machine is a valuable material science and engineering tool. It allows engineers and scientists to test how well materials resist scratches under controlled conditions and, based on these results, select suitable materials for specific applications.
Also read about: ASTM D6037 Dry Abrasion Mar Resistance of Glass Coating
FAQs on ASTM G65 Test
The ASTM G65 test simulates sliding abrasion conditions under moderate pressure. It uses dry sand metered between a rubber wheel and a block coupon of the material being evaluated.
Abrasion testing can provide data on material resistance under laboratory-controlled conditions.
The ASTM G 65 dry-sand rubber wheel test is a famous low-stress abrasion test in the USA.
This test measures the hardness of aggregates and determines whether they are suitable for different pavement construction works.
The Martindale Abrasion Tester's working principle involves subjecting fabric samples to a controlled rubbing action against a standard abrasive medium.
Talk to Our Experts Today!
Submit your contact info and we’ll get back to you within 24 hours
Full Spectrum of ASTM Material Testing — Backed by 2,000+ Trusted Lab Partners
ASTM standards for chemical composition, physical properties, failure analysis, and other routine and non-routine testing for polymers and plastics
ASTM standards for determination of mechanical, physical, and thermal properties, and performance of monolithic and composite ceramics
ASTM standards guiding various destructive, non-destructive and analytical tests for quality control of different metals and alloys
ASTM standards for chemical analysis of solid, liquid and gaseous materials for specification compliance and quality control
ASTM standards for various chemical, physical, stability and exposure analysis of paints and coatings
Our Services

Metrology
A variety of microscopy and spectroscopy tools available for precise measurements from the nano to the meter scale.
Learn More
Materials Testing
ASTM and ISO standard and custom chemical, mechanical, thermal, corrosion tests, etc. for all materials metals, ceramic or polymers.
Learn More
Product Testing
Thousands of tests for product quality and reliability under heat, humidity, temperature shock, vibration, drop, electrostatic discharge.
Learn More
