Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) Introduction
What is Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)?
Understanding on Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) is a thermal analysis technique that helps measure a sample’s mass as a function of time or temperature when the sample is treated in a specific temperature program in a controlled environment. For example, thermogravimetric analysis of polymers provides valuable quantitative data on a material’s physical and chemical characteristics, such as dehydration, breakdown, oxidation, and reduction.
Types of Thermogravimetric Analysis
There are three variants: dynamic Thermogravimetric Analysis, static Thermogravimetric Analysis, and quasistatic Thermogravimetric Analysis. Dynamic TGA involves the temperature rising while mass data is collected, while static TGA measures mass at a fixed temperature. Quasistatic TGA involves heating and stabilizing the sample until its mass stabilizes.
Thermogravimetric Analysis Instrumentation
The instrumentation of Thermo gravimetric analysis includes various components that help in the overall process of detecting weight loss.
- Microbalance: the highly sensitive microbalance measures the weight loss percentage due to temperature changes.
- Holder: The sample is placed in a crucible made of materials resistant to high temperatures, such as platinum and quartz.
- Furnace: It is responsible for the temperature change of a sample at a controlled rate.
- Gas Manager: TGA equipment frequently employs a controlled atmosphere, inert (like nitrogen or argon) or reactive (like oxygen), to imitate diverse environmental conditions throughout the study.
- Software Analysis: Both the new and conventional TGA instruments contain a variety of software that enable the study of real-time data. These software programs are also useful for interpreting results such as decomposition steps, kinetic parameters, and residue.
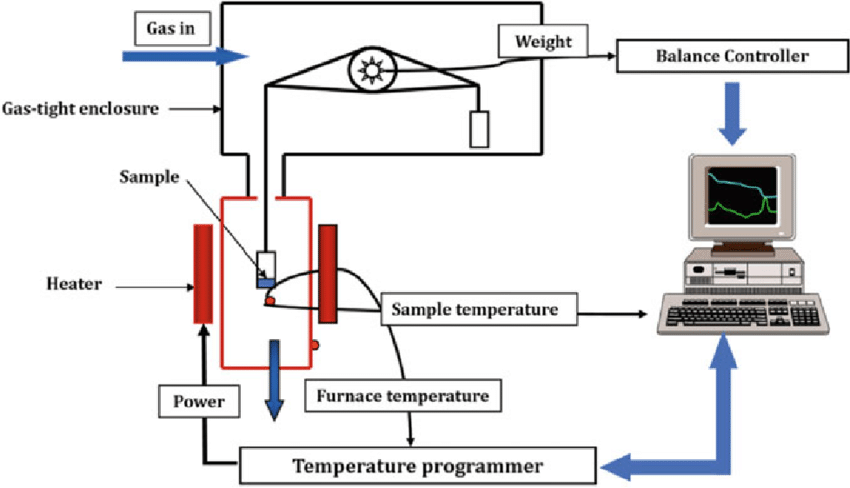
Working Principle of TGA
Thermogravimetric Analysis is a metrology testing method used to weigh the mass of a sample as it is heated in a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere. It involves removing gaseous byproducts and monitoring the resulting changes in the sample’s mass.
Strengths and Limitations of TGA
The following are some of the strengths and limitations of TGA:
| Strength | Limitations |
| Accurate rate of weight loss in polymers | Sample size (50 milligrams) |
| Shrinkage and melting behavior can be accessed | Atmospheric conditioning should be maintained |
| Shrinkage and melting behavior can be accessed | Analysis time is one hour |
Applications of TGA & Industries Employed
The following are some of the applications & industries employed in thermogravimetric analysis:
| Applications | Industries |
| Decomposition studies | Pharmaceutical Industry |
| Content analysis | Automotive Industry |
| Evaporation and desorption | Aerospace Industry |
| Oxidation studies | Polymer industry |
| Lifetime estimation | Food Industry |
| Reaction kinetics | Material Science and Research |
Conclusion
Understanding on Thermogravimetric Analysis is essential for designing materials that survive high temperatures, as devices produced from the material may break down after extended usage. Additionally, derivative thermogravimetric analysis (DTG) can enhance the interpretation of weight loss events by providing the rate of mass change as a function of temperature. Thermogravimetric Analysis equipment can also be modified to include differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to track possible phase transitions. Furthermore, explore ASTM E1131 and ISO 11358 for detailed guidelines on Thermogravimetric Analysis.
FAQs on Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
Solid raw materials
A minimum of 50 mg is required for TGA sample analysis.
Yes, TGA is used in the textile industry to access the thermal properties of natural and synthetic fibers.
There are three variants: Dynamic Thermogravimetric Analysis, Static Thermogravimetric Analysis, & Quasi-Static Thermogravimetric Analysis
In environmental chemistry, TGA is employed in determining the character and thermal property of solid waste in the processes of waste disposal and recycling.
Talk to Our Experts Today!
Submit your contact info and we’ll get back to you within 24 hours
Full Spectrum of ASTM Material Testing — Backed by 2,000+ Trusted Lab Partners
ASTM standards for chemical composition, physical properties, failure analysis, and other routine and non-routine testing for polymers and plastics
ASTM standards for determination of mechanical, physical, and thermal properties, and performance of monolithic and composite ceramics
ASTM standards guiding various destructive, non-destructive and analytical tests for quality control of different metals and alloys
ASTM standards for chemical analysis of solid, liquid and gaseous materials for specification compliance and quality control
ASTM standards for various chemical, physical, stability and exposure analysis of paints and coatings
Our Services

Metrology
A variety of microscopy and spectroscopy tools available for precise measurements from the nano to the meter scale.
Learn More
Materials Testing
ASTM and ISO standard and custom chemical, mechanical, thermal, corrosion tests, etc. for all materials metals, ceramic or polymers.
Learn More
Product Testing
Thousands of tests for product quality and reliability under heat, humidity, temperature shock, vibration, drop, electrostatic discharge.
Learn More
