Introduction
ASTM F22, commonly called the “Water-Break Test for Hydrophobic Surface Films,” is one of the standardized test methods for determining the cleanliness of metal surfaces by detecting hydrophobic contaminants. The test involves the application of water on the prepared metal surface, which is then observed. If the water spreads uniformly, the surface is clean; if it beads up or breaks into droplets, these films or contaminants contain hydrophobic materials. This technique is widely applied in industries where surface cleanliness is vital. Some examples include the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries, which produce pharmaceuticals and must ensure that their equipment is clean.
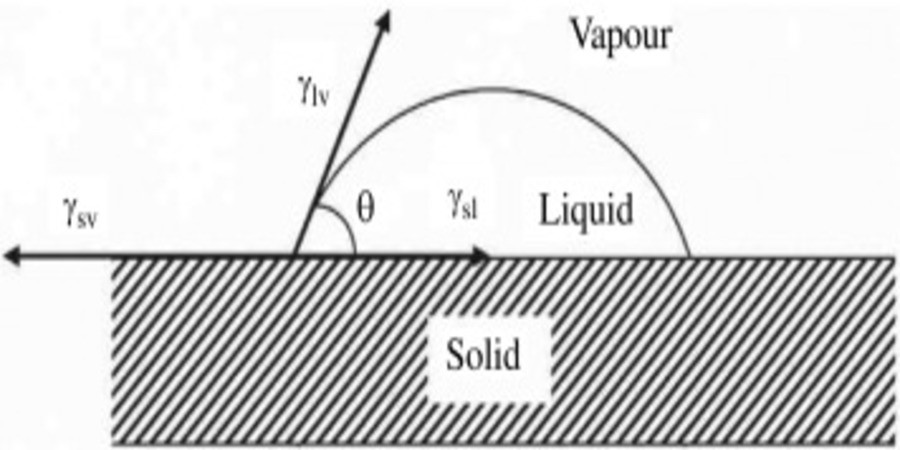
Scope
The ASTM F22 test method determines whether a hydrophobic film is on the surface and whether a hydrophobic organic material is in the processing environment. It aids in identifying the presence of hydrophobic organic pollutants that might be attached to metal surfaces. Test results may be grossly biased and unreliable across a rough or porous surface.
Test Procedure
A small portion of the specimen can be placed at an angle. The surface of the specimen is sprayed with a mist of distilled water. This is done to check whether the water flows freely on the surface without any water droplets staying on it. If it does, it’s a clean surface without contamination. But if the water droplets sit on it and do not flow through, then the surface of the specimen is contaminated.
Surface wetting measurements: Standard test methods C813, D5946, ED7490, and Practice D7334 show some measurement methods based on contact angle.
ASTM F22 Specimens
| Sample Size | Surface Area: Larger surfaces may require multiple test areas to ensure consistent cleanliness. Criticality of the Surface: Critical components may require more extensive testing. Process Control: Testing multiple samples from different stages or batches might be necessary if used for process control. |
Result Analysis
Since this method is not quantitative, the report will include whether or not the surface film has a hydrophobic contaminant.
- It should be noted that the test’s sensitivity varies with the level of airborne contaminant and the duration of exposure to the specimen surface.
- This test procedure is not feasible for assembled hardware, where there is a risk of water entrapment in complex surface structures that may not be effectively removed.
Read more: Analysis of Contaminant Films
Pros and Cons of ASTM F22 Testing
The following are some of the pros & cons of ASTM F22 testing:
| Advantages | Limitations |
| Non-Destructive: The test doesn’t influence the surface and can be used without damaging components or altering their final qualities. | Subjective Results: Because it is based on visual inspection, the test is subjective and reliant on the operator’s experience and judgment. Different operators may interpret results differently. |
| Effective for Large Surfaces: The size of the examined component does not limit it and can be used on relatively large surfaces. | Limited Sensitivity: Very thin or low amounts of contamination that don’t significantly affect water beading can go undetected by the test. Minimal levels of contaminants could go undetected. |
| Immediate Indication of Hydrophobic Films: Water will bead up instead of flowing out as a film on the surface that is hydrophobic, greasy, or dirty. This makes the appearance of contaminants easier to distinguish. | Not Suitable for All Materials: It will be useful when applied to metallic surfaces. However, it would not work so well on some non-metallic materials or surfaces that have already been classified as hydrophobic naturally. |
| Quick Results: This is suitable for applications with high production environments since it offers immediate feedback to the operators about the surface’s cleanliness or polluted status. | Affected by Environmental Conditions: Factors such as temperature, humidity, or water quality used for the experiments will affect the results since they can influence how the water behaves on the surface. |
Conclusion
This is an ASTM F22 Water-break Test, a qualitative process that detects whether or not hydrophobic surface films exist on metallic surfaces and whether or not they are effective. This test procedure is most often used to establish whether the surface contamination covering the metal surfaces is absent because it prevents any further surface treatments, such as priming, anodizing, conversion coating, plating, or adhesive bonding.
FAQs
Water Resistance Testing of Coatings in 100% Relative Humidity (ASTM D 2247): Water resistance testing of painted or coated panels is accomplished by placing them in an enclosed chamber containing a heated, saturated mixture of air and water vapor. The chamber's temperature is usually maintained at 100° F (38° C).
The specimens are dried in an oven for a specified time and temperature for the water absorption test and then placed in a desiccator to cool. Immediately upon cooling, the specimens are weighed. The material then emerges in water at agreed-upon conditions, often 23°C, for 24 hours or until equilibrium.
ASTM F22 Water break tests are used primarily for metal surfaces to identify surface contaminants on incoming raw materials or after surface processes, such as cleaning processes, etching, anodizing, painting, priming, coating, grit-blasting, or sanding, have occurred.
The water break check simply involves flooding a clean surface similar to those inspected and observing the surface film. A sufficient wetting agent is present if a continuous film forms over the entire surface.
Talk to Our Experts Today!
Submit your contact info and we’ll get back to you within 24 hours
Full Spectrum of ASTM Material Testing — Backed by 2,000+ Trusted Lab Partners
ASTM standards for chemical composition, physical properties, failure analysis, and other routine and non-routine testing for polymers and plastics
ASTM standards for determination of mechanical, physical, and thermal properties, and performance of monolithic and composite ceramics
ASTM standards guiding various destructive, non-destructive and analytical tests for quality control of different metals and alloys
ASTM standards for chemical analysis of solid, liquid and gaseous materials for specification compliance and quality control
ASTM standards for various chemical, physical, stability and exposure analysis of paints and coatings
Our Services

Metrology
A variety of microscopy and spectroscopy tools available for precise measurements from the nano to the meter scale.
Learn More
Materials Testing
ASTM and ISO standard and custom chemical, mechanical, thermal, corrosion tests, etc. for all materials metals, ceramic or polymers.
Learn More
Product Testing
Thousands of tests for product quality and reliability under heat, humidity, temperature shock, vibration, drop, electrostatic discharge.
Learn More
