Introduction:
ASTM E1876 is a standard test usually used to measure dynamic Young’s modulus, shear modulus, and Poisson’s ratio for materials through the impulse excitation of vibration. This test is applicable for measuring the elastic properties of almost all kinds of materials, such as metallic, ceramics, composites, and some polymers. The test works by having a specimen subjected to a small, controlled mechanical impact, which causes the material to vibrate. The resulting vibrations are analyzed to accurately determine the attached material’s stiffness, frictional resistance to shearing deformation, and the relation between axial and lateral strains in the sample. Knowledge and determination of these properties become crucial for understanding the mechanical behavior of these materials under various stress conditions. They are essential for industrial applications where the material’s performance must be considered with utmost precision, such as in aerospace, automotive, and civil engineering.
Scope of ASTM E1876 Test:
ASTM E1876 test method is used for material development, characterization, design data generation, and quality control purposes. This test is used for elastic, isotropic, and homogeneous materials. Specimens of these materials possess specific mechanical resonant frequencies. Resonance frequency depends upon the mass, elastic moduli, and geometry of a suitable test specimen, such as those with rectangular or cylindrical shapes. Thus, knowing these parameters is essential for calculating a material’s resonance frequency. Subsequently, these resonance frequency values can be utilized to determine the dynamic elastic properties of the material.
The Dynamic Young’s modulus, also known as the modulus of rigidity, is determined using the resonance frequency in the flexural or longitudinal vibration mode. In contrast, the dynamic shear modulus, which is also referred to as the modulus of rigidity, is determined through torsional resonance vibrations. Consequently, both Young’s and shear modulus compute Poisson’s ratio.
The ASTM E1876 test method is also performed at extremely low and high temperatures with suitable equipment modifications and appropriate modifications to the calculations to compensate for thermal expansion.
ASTM E1876 Test Procedure:
The ASTM E1876 The test method determines elastic properties by calculating resonance frequencies. Specifically, test specimens’ resonance frequencies are identified by exciting them at various frequencies to find a particular frequency that matches the specimen’s natural resonance frequency. Consequently, this process involves a hit-and-trial approach.
This test method measures the fundamental resonant frequency of test specimens of suitable geometry by mechanically exciting them with a singular elastic strike with an impulse tool. The signals are analyzed, and the fundamental resonant frequency is isolated and measured by the signal analyzer, which provides a numerical reading that is (or is proportional to) either the frequency or the period of the specimen vibration. The dimensions of the specimen, its resonance frequency, and mass are used to calculate Young’s modulus and shear’s modulus.
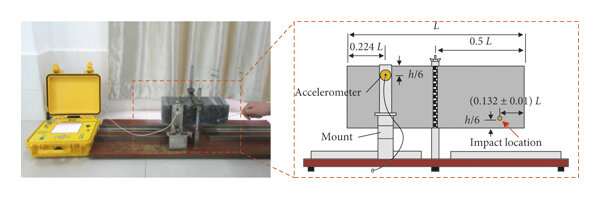
Specimen Size:
For ASTM E1876, the specimens should be either rectangular or circular. Both can be used to calculate elastic properties.
Result Analysis:
The following data is analyzed in ASTM E1876:
| Parameters | Descriptions |
| Young modulus | Y = (38.3 × f2 × ρ × ℓ4)/d2 Where: Y = Young’s modulus f = resonance frequency of oscillations ρ = density ℓ = length d = width |
| Shear modulus | E = 2G(1 + ν) Where: E = Young’s modulus G = shear modulus ν = Poisson’s ratio |
| Poisson’s ratio | µ = (E/2G) – 1 Where: µ = Poisson’s ratio E = Young’s modulus G = shear modulus |
| Moduli at elevated and cryogenic temperatures | Where: MT = modulus at temperature T M0 = modulus at room temperature fT = resonant frequency in a furnace or cryogenic chamber at temperature T fO = resonant frequency at room temperature in a furnace or cryogenic chamber, α = average linear thermal expansion from room temperature to test temperature ∆T = temperature differential in °C between the test temperature T and room temperature |
Conclusion:
Essential uses of this test method under ASTM E1876 abound across many industries. For instance, in material development, this test method is employed to provide crucial data that aids in creating new materials with specific mechanical properties. This test method characterizes materials by accurately determining dynamic Young’s modulus, shear modulus, and Poisson’s ratio; thus, it helps the researcher/engineer realize how different materials will act under various circumstances. Results obtained from ASTM E1876 are crucial for design applications. Indeed, this standard provides very precise and reliable information, which can then be used to predict the performance of materials in actual applications. Consequently, it ensures safety, performance, and durability.
FAQs
ASTM E1876 is a standardized test method used to determine the dynamic Young's modulus, shear modulus, and Poisson's ratio of materials by impulse excitation of vibration.
ASTM E1876 applies to various materials, including metals, ceramics, composites, and specific polymers.
The ASTM E1876 test method is widely used in material development, characterization, design data generation, and quality control.
Yes, ASTM E1876 is a valuable tool for quality control. It allows manufacturers to verify that materials meet the required mechanical properties before they are used in production, ensuring consistency and reliability in the final products.
While ASTM E1876 provides accurate measurements of elastic properties, it may not be suitable for materials that do not exhibit well-defined resonance frequencies or for those with complex internal structures that significantly dampen vibrations.
Talk to Our Experts Today!
Submit your contact info and we’ll get back to you within 24 hours
Full Spectrum of ASTM Material Testing — Backed by 2,000+ Trusted Lab Partners
ASTM standards for chemical composition, physical properties, failure analysis, and other routine and non-routine testing for polymers and plastics
ASTM standards for determination of mechanical, physical, and thermal properties, and performance of monolithic and composite ceramics
ASTM standards guiding various destructive, non-destructive and analytical tests for quality control of different metals and alloys
ASTM standards for chemical analysis of solid, liquid and gaseous materials for specification compliance and quality control
ASTM standards for various chemical, physical, stability and exposure analysis of paints and coatings
Our Services

Metrology
A variety of microscopy and spectroscopy tools available for precise measurements from the nano to the meter scale.
Learn More
Materials Testing
ASTM and ISO standard and custom chemical, mechanical, thermal, corrosion tests, etc. for all materials metals, ceramic or polymers.
Learn More
Product Testing
Thousands of tests for product quality and reliability under heat, humidity, temperature shock, vibration, drop, electrostatic discharge.
Learn More
